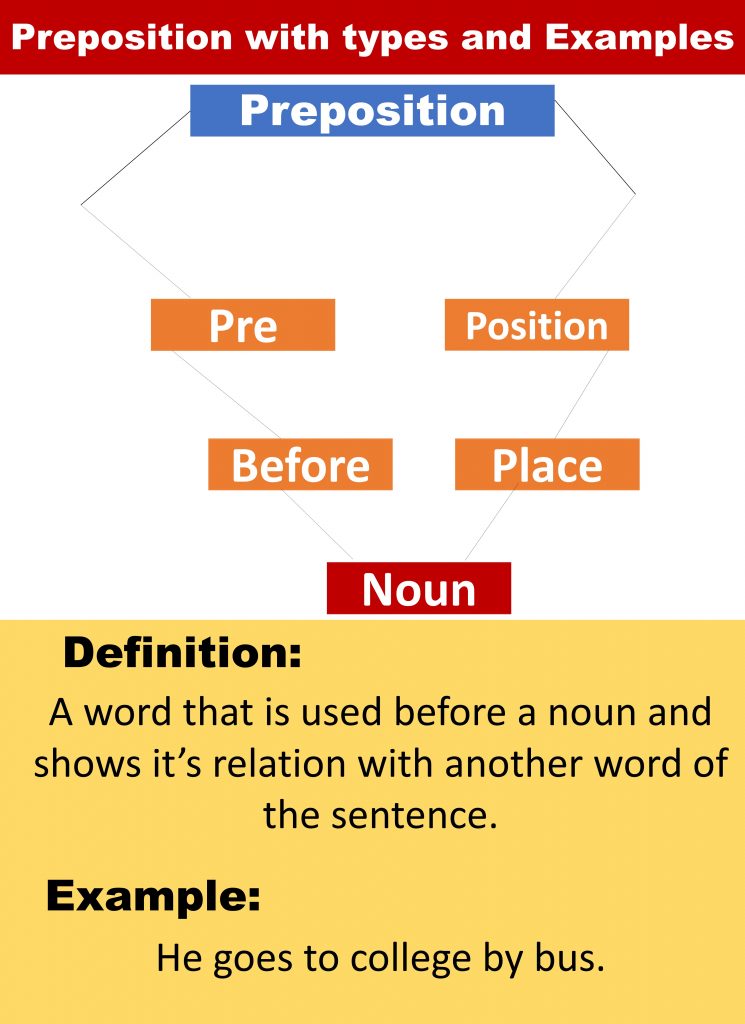
Definition and meaning of Preposition
A preposition is a word – and almost always a very small, very common- that shows direction, location, or time or that introduces an object.
Simply, a word that is used before a noun and shows its relation with another word of the sentence.
Examples:
at, by, for, from, in, of, onto, into, except, inside, instead of.
He goes to college by bus.
Why Prepositions are Essential for English Grammar?
We know that we can’t become a professional in our field without the English language. If we want to up in our life and then we have to learn the English language. If we will learn the English language and we can easily achieve our life destination.
You will be taught how will we learn the English language? The first and most important thing is English Grammar for your English speaking. And that’s why today we are going to learn prepositions and their types with Urdu to English examples.
Prepositions are tricky little beasts. The relative shortness of the words and their often misplaced role in the overall scheme of things means that we should treat them carefully and perhaps give them more time in the classroom than is usually in the case.
Some important rules for Prepositions
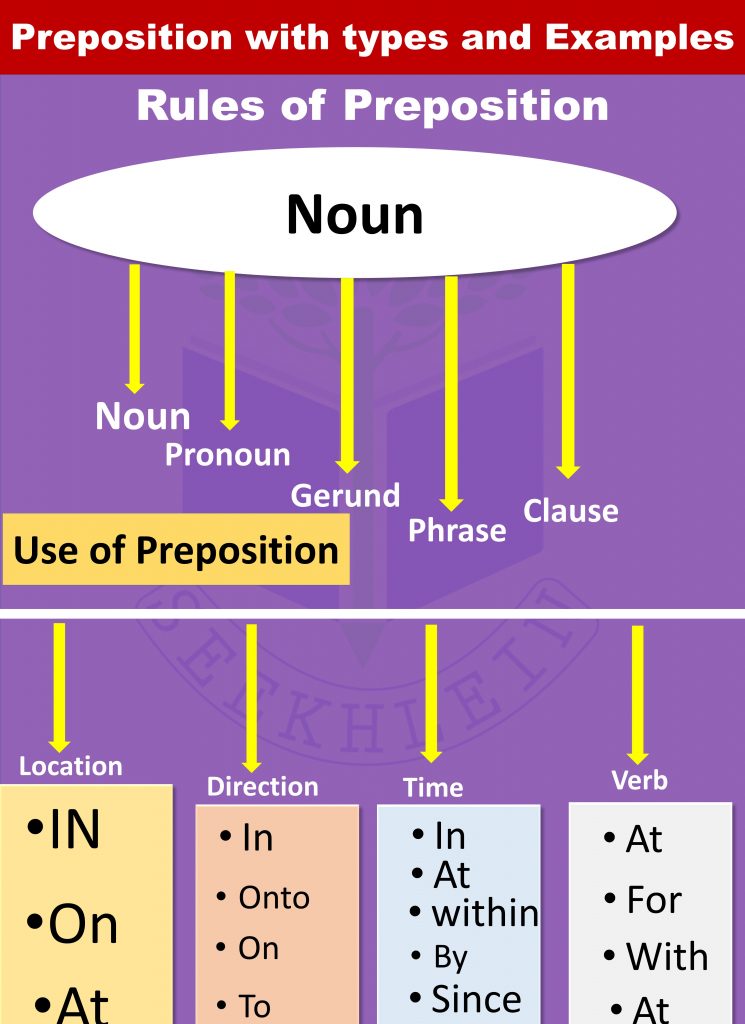
Rule 1: Preposition must relate to noun or pronoun in the sentence.
- It is not necessary that preposition must always come before a noun or pronoun, instead, it must be closely related to the noun or pronoun in the sentence.
Examples:
I put the things in the box.
Where are you from?
That is something he can’t agree with.
Whom did you talk to?
Rule 2: The pronoun after the preposition must be an object
- The pronoun after the preposition should be an object form.
- It should be an objective pronoun, not a subjective pronoun.
Examples:
The present was from him.
The meeting was attended by her.
She gave it to them.
This is from my friend and me.
| Subject Pronoun | Object Pronoun |
| I | Me |
| You | You |
| He | Him |
| She | Her |
| It | It |
| We | Us |
| They | Them |
Rule 3: A verb can not become a prepositional object.
Examples:
He is bad at keep promises.
They are talented in the hunt.
She is good at solve problems.
He insisted on try again.
He prevented me from drink cold water.
The inspector walked into the build.
She is interested in improving herself.
Rule 4: Verb placed after a preposition should be in gerund form.
- Verb placed immediately after preposition must be in gerund form.
Definition of Gerund
The gerund is a word that looks like an” ing” form of a verb, but it acts as a noun in a sentence.
- Gerund acts as both verb and noun
Examples:
Running is a fan.
His hobby is hunting.
Smoking is injurious to health.
He is very good at painting.
Lying is a bad habit.
Swimming is my hobby.
Rule 5: Do not confuse the preposition ‘to’ with infinitive ‘to’.
- ‘ To’ is an infinitive as well as a preposition.
- If to is followed immediately by a simple verb, it is a part of an infinitive.
- It is followed by a noun construction, it is a preposition.
Examples:
I am used to running.
I look forward to seeing you.
I used to live in London.
They love to sing.
Rule 6: When an object of the preposition is an interrogative pronoun like, Who, What, Whom, Which, Where, etc the preposition takes front or end position.
Examples:
Who are you talking to?
By which bus did you come?
Where are you from?
For whom were instructions given?
What are you thinking of?
Use of Prepositions
Types of Preposition
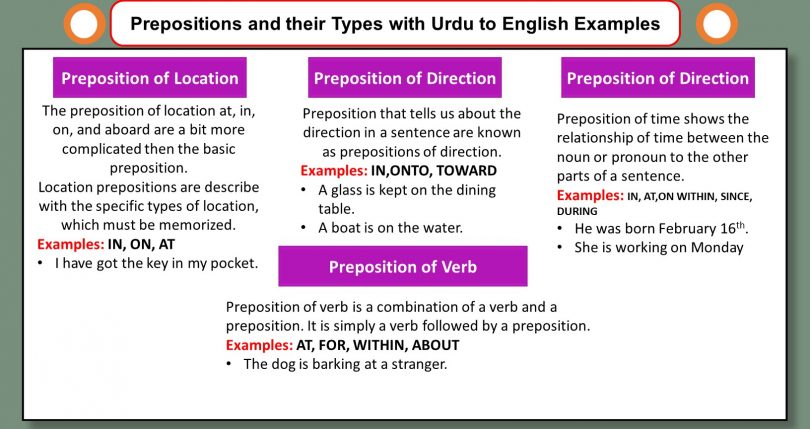
Preposition of Location
Preposition of Direction
Preposition of Time
Preposition of Verb
Preposition of Location
Definition:
The preposition of the location at, in, on, and aboard are a bit more complicated than the basic position preposition. Location prepositions are associated with specific types of location, which must be memorized.
Examples
- In
- On
- At
Preposition of Direction
Definition:
Prepositions that tell us about the direction in a sentence are known as Prepositions of Direction.
Examples
- In
- On
- Onto
- To
- Toward
We are going to home.
She threw a ball into the water.
Preposition of Time
Definition:
Preposition of time shows the relationship of time between the noun or pronoun to the other parts of a sentence.
Examples
- In
- At
- Within
- By
- Since
- For
- During
Preposition of Verb
Definition:
A preposition verb is a combination of a verb and a preposition. It is simply a verb followed by a preposition.
Examples
- At
- For
- With
- About
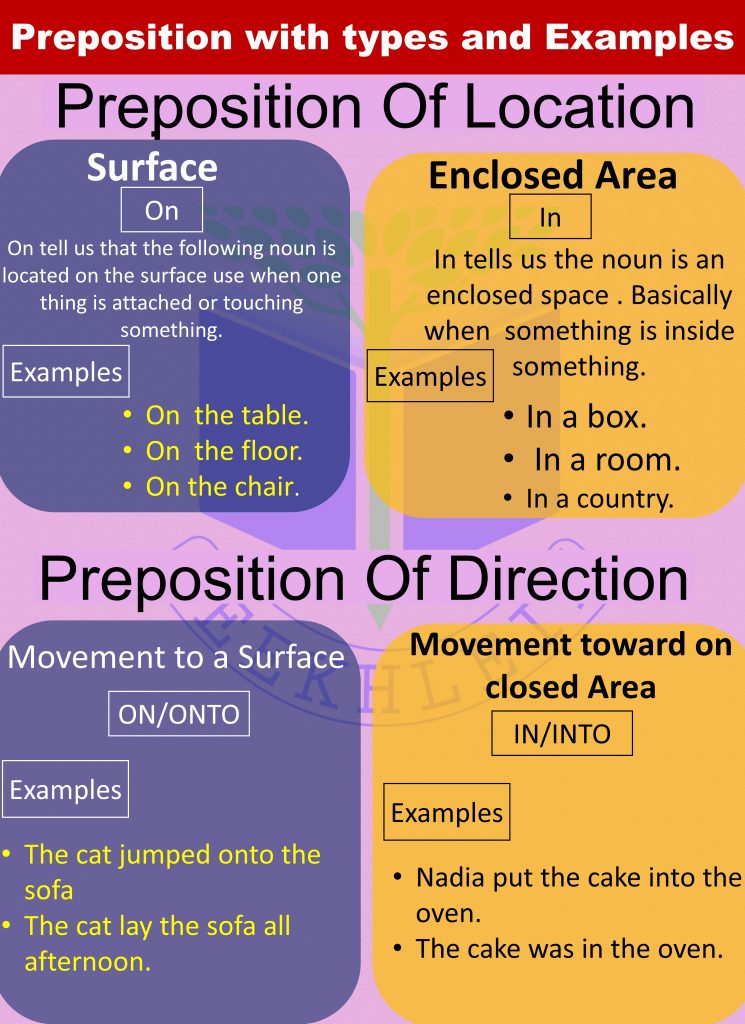
 Preposition of Location
Preposition of Location
Types:
- Surface
- Enclosed Area
- Point
Surface:
Use of On
On tell us that the following noun is located on the surface use when one thing is attached or touching something.
Examples
- On the table.
- On the floor.
- On the chair
The school is on Bay Street.
سکول بے اسٹری پر ہے۔
The author’s name is on the cover of the book.
مصنف کا نام کتاب کے کے کور پر لکھا ہے۔
There are no prices on this menu.
اس مینو میں کوئی قیمت نہیں ہے۔
You are standing on my foot.
آپ میرے پاؤں پر کھڑے ہیں۔
There was a no-smoking sign on the wall.
دیوار پر سگریٹ نوشی کا نشان نہیں تھا۔
I live on the 7th floor.
میں ساتوے فلور پر رہتا ہوں۔
A picture is on the wall.
دیوار پر ایک تصویر ہے۔
A book is kept on the table.
ایک کتاب میز پر رکھی ہوئی ہے۔
A glass is kept on the dining table.
ایک گلاس کھانے کے ٹیبل پر رکھا ہوا ہے۔
The clock is on the wall.
گھڑی دیوار پر ہے۔
A boat is on the water.
ایک کشتی پانی پر ہے۔
A ball is kept on the desk.
ایک گیند ڈیسک پر کھا ہوا ہے۔
Note:
If the object is not touched the surface, ON will not be used.
Enclosed Area
Use of In
It tells us the noun is an enclosed space. Basically when something is inside something.
Examples:
- In a box.
- In a room.
- In a country.
I have got the key in my pocket.
مییری جیب میں چابی مل گئی ہے۔
There is some milk in the fridge.
فریج کچھ دودھ ہے۔
She left it in the top drawer۔
اس نے اسے اوپر والے دراز میں چھوڑ دیا۔
There is nothing left in my cup.
میرے کپ میں کچھ نہیں بچا ہے۔
I am in the car.
میں کار میں ہوں۔
Can you take a seat in the waiting room, please?
کیا آپ ویٹنگ روم میں سیٹ لے سکتے ہیں۔
I have left my bag in your office.
میں نے اپنا بیگ تمہارے دفتر میں چھوڑ دیا ہے۔
Why don’t we have a picnic in the park?
ہمارے پاس پارک میں پکنک کیوں نہیں ہے؟
I am filming this video in Pakistan.
میں یہ ویڈیو پاکستان میں فلم بنا رہا ہوں۔
I grew up in Melbourne.
میں میلبورن میں پلا بڑھا ۔
Holidaying in Pakistan is easy if you speak Urdu.
اگر آپ اردو بولتے ہیں تو پاکستان میں تعطیلات آسان ہیں۔
We are going for a drive in the country.
ہم ملک میں مہم چلانے جارہے ہیں۔
Lots of people were swimming in the lake.
بہت سارے لوگ جھیل میں تیر رہے تھے۔
She works in the finance team.
وہ فنانس ٹیم میں کام کرتی ہے۔
He’s got selected to play in the national team.
وہ قومی ٹیم میں کھیلنے کے لیے منتخب ہو گیا ہے۔
Careful! There’s a lot of chili in that sauce.
ہوشیار اس چٹنی میں مرچ بہت تیز ہے۔
There’s a lot of sugar in soft drinks.
سوفٹ پانی میں نمک بہت تیز ہے۔
Do your work in an office?
کیا تم دفتر میں کام کرتے ہو؟
I have a meeting in Multan.
میری ملتان میں ایک میٹنگ ہے۔
Jupiter is in the Solar system.
جیوپیٹر سولر سسٹم میں ہے۔
Do you live in Punjab?
کیا تم پنجاب میں رہتی ہو؟
Point
Use of At
It tells us that the following noun is located at a specific point or location. It shows an exact position.
Examples:
Ali’s still at the school.
علی ابھی سکول میں ہے۔
She’s waiting at the entrance.
وہ دروازے پر انتظار کر رہی ہے۔
I will meet you at the bus stop.
میں آپ سے بس سٹاپ پر ملوں گا۔
Turn left at the traffic light.
ٹریفک لائٹ سے بائیں مڑیں۔
I studied Design at the college.
میں نے کالج میں ڈیزان کی تعلیم حاصل کی۔
Let’s meet at the station.
سٹیشن پر ملتے ہیں۔
We have to stop at the supermarket on the way home.
ہمیں گھر کے راستے میں سپر مارکیٹ میں رکنا ہے۔
There was a crazy guy at the library today.
آج لائبریری میں ایک پاگل آدمی تھا۔
They live at 14, University road.
I will meet you at the corner of Beach Street and Park Road.
میں آپ کو بیچ سٹیریٹ اور پارک روڈ کے کونے میں ملوں گا۔
I had a coffee at Bilal’s house.
میں بلال کے گھر میں ایک کافی پی تھی۔
We meet at a party.
ہم پارٹی پے ملتے ہین۔
He is speaking at the conference later this week.
وہ اس ہفتے کے آخر میں سے خطاب کررہا ہے۔
List for Preposition of Location
| At Point | In Closed Space | On Surface |
| at the corner | in the garden | on the wall |
| at the bus stop | in London | on the ceiling |
| at the top of the page | in a box | on the cover |
| at the door | in France | on the door |
| at the end of the road | in my pocket | on the floor |
| at the entrance | in my wallet | on the carpet |
| at the crossroads | in a building | on the menu |
| at the front of the desk | in a car | on a page |
Preposition Of Direction
Types
- The movement to a Surface
- The movement toward on closed Area
- The movement to a destination
The movement to a Surface
Use of ON/ONTO
ON
To indicate someone or something is on the surface of a thing, on top of it.
Examples
The cat lay on the sofa all afternoon.
بلی ساری دوپہر صوفے پر پڑی۔
A fly settled on my bread while I was eating it.
جب میں اسے کھا رہا تھا تو ایک مکھی میری روٹی پر بس گئی۔
Use of on for Device
He is on the phone
وہ فون پر ہے۔
The show will be telecasted on television.
شو ٹیلی ویثزن پر دکھایا جائے گا۔
He is solving the sum on the calculator.
وہ کلکولیٹر پر جمع کر رہا ہے۔
Use of On for Body Parts
My mother kissed me on the forehead.
میری امی نے مجھے پیشانی سے چوما۔
The ice cream fell on my leg.
آئس کریم میری ٹانگ پر گری۔
She wears her engagement ring on her finger.
وہ اپنی منگنی کی انگھوٹھی اپنی انگلی میں پہنتی ہے۔
Use of Onto
To indicate a movement on the surface of a thing
The cat jumped onto the sofa.
بلی صوفے پر کود گئی۔
Move the books onto the shelf.
کتابیں پر شلف منتقل کریں۔
She climbed onto the roof.
وہ چھت پر چڑھ گئی۔
He stepped down from the train onto the platform.
وہ ٹرین سے نیچے پلیٹ فارم پر آگیا ۔
Let’s step onto the dance floor.
آئیے ڈانس فلور پر قدم رکھیں۔
Ali climbed onto the back of the truck.
علی ٹرک کے پچھلے حصے پر چڑھ گیا۔
Bilal jumped onto the mat.
بلال چٹائی پر کو گیا
Ahmad fell onto the floor.
احمد چھت پر گر گیا۔
The movement toward on closed Area
Use of IN/INTO
IN
Something that is enclosed or surrounded by something else appears to be too enclosed or surrounded.
Examples:
The cake was in the oven.
کیک اوون میں تھا ۔
The vegetables are in the fridge.
سبزیاں فریج میں ہیں۔
The key is in the pocket.
چابی جیب میں ہے۔
The mobile is in the box.
موبائل باکس میں ہے۔
Ali is cooking in the kitchen.
علی کچن میں کھانے پکا رہا ہے۔
Use of INTO
From outside to inside
Examples:
I put the milk into the pot.
میں نے دودھ کو برتن میں ڈال دیا۔
Put the tea into the cup.
چائے کپ میں ڈال دو۔
He jumped into the river.
اس نے دریا میں چھلانگ لگائی۔
He jumped into the water.
اس نے پانی میں چھلانگ لگائی۔
Ali is going into the kitchen.
علی کچن میں جارہا ہے۔
The man is jumping into the pool.
آدمی پول میں چھلانگ لگا رہا ہے۔
His mobile is putting into the pocket.
اس کا موبائل جیب میں ڈال رہا ہے۔
She pouring water into the bucket.
وہ بالٹی میں ڈال رہی ہے۔
A cow ran into the street.
ایک گلی میں دوڑ گئی۔
I saw a dirty dog coming into the garden.
میں نے دیکھا کہ ایک گندا باغ میں آ رہا ہے۔
Milk turns into cheese.
دودھ پنیر میں بدل جاتا ہے۔
Milk is turning into curd.
دودھ دہی میں بدل رہا ہے۔
The color of that shirt changed into yellow color.
اس شرٹ کا رنگ پیلے رنگ میں بدل گیا۔
Movement to Destination
Use of TO
To denotes movement to a fixed place destination.
Examples:
I am going to Lahore.
میں لاہور جا رہا ہوں۔
She is coming to me.
وہ میرے پاس آ رہی ہے۔
We are heading to the entrance of the building.
She is giving money to him.
وہ اس کو پیسے دے رہی ہے۔
He went to school.
وہ سکول گیا۔
Today we are going to market.
آج ہم مارکیٹ جا رہے ہیں۔
Tomorrow we are coming to you.
کل ہم آپ کے پاس آ رہے ہیں۔
Alis is going to do this.
علی یہ کرنے جا رہا ہے۔
Are you listening to me?
کیا آپ مجھے سن رہی ہیں۔
He went to school.
وہ سکول گیا۔
The Pakistani team is going to play.
پاکستانی ٹیم کھیلنے جا رہی ہے۔
Use of ONTO
Denotes the direction of movement.
He went towards the school.
وہ سکول کی طرف گیا۔
Could you tell me the way towards the station?
کیا آپ مجھے سٹیشن کی طرف جانے کا راستہ بتا سکتے ہیں؟
A snake was coming towards me.
ایک سانپ میری طرف آ رہا تھا۔
He turned towards the mirror.
وہ آئینے کی طرف مڑا۔
She is walking towards the library.
وہ لائبریری کی طرف چل رہی تھی۔
Ali is coming towards our home.
علی ہمارے گھر کی طرف آ رہا ہے۔
I am going towards my village.
میں گاؤں کی طرف جا رہا ہوں۔
Preposition Of Time
Types
- Point
- Extended
Point
- On
- In
- At
Use of On
| Days of the week | On Mondays
|
| Dates | On ( the) 5th of 6 June |
| Particular days | Particular days |
More Examples
She is working on Monday.
وہ پیر کو کام کر رہی ہے۔
She usually works on Mondays.
وہ عام طور پر پیر کے روز کام کرتی ہے۔
We are going to the theater on Wednesday evening.
ہم بدھ کی شام تھیٹر جا رہے ہیں۔
The interview is on 29th April.
انٹرویو 29 اپریل کو ہے۔
He was born on February 16th.
وہ 16 فروری کو پیدا ہوا تھا۔
She was born on Valentine’s day.
وہ ویلنٹائن کے دن پیدا ہوئی تھی۔
I have an exam on my birthday.
میری سالگرہ کے دن میرا ایک امتحان ہے۔
What are you doing on New Year’s Day?
نئے سال کے دن آپ کیا کررہے ہیں؟
What are you doing on the weekend?
آپ ہفتے کے آخر میں کیا کر رہے ہیں؟
The class will be held on Monday.
کلاس پیر کو ہوگی۔
I will visit you on Wednesday.
میں آپ کے پاس پیر کو آوں گا۔
Where are you on Friday?
جمعے کے دن آپ کہاں ہیں؟
He does not work on Sundays.
وہ پیر کے دن کام نہیں کرتی ہے۔
Use of In
| Part of the day | In the morning |
| Month | In December |
| Seasons | In Winter |
| Years | In 2021 |
| Centuries | In the 1990 |
More examples
My birthday is in Junary.
I am going on vacation in August.
Halloween is in October.
Ali was born in 2001.
The Titanic sank in 1912.
The treaty was signed in 1840.
Life was difficult in the 1940s.
There were many hippies in the ’60s.
We are living in the 21st century.
It was built in the sixth century.
We go to the beach in summer.
Does it snow here in winter?
There are many flowers in Spring.
Use of At
| Night | At night |
| Clock | at 7 O’clock |
| Holidays | at Christmas
at the weekend |
Mor Examples
I get up at 7 O’clock.
میں سات بجے اٹھتا ہوں۔
The movie at starts at 8:30
فلم کا آغاز ساڑھے بجے ہوگا۔
We arrived home at midnight.
ہم آدھی رات کو گھر پہنچے۔
Did you eat much at Easter?
کیا آپ نے ایسٹر پر زیادہ کھانا کھایا؟
The train arrives at 3:30۔
ٹرین ساڑھے تین بجے پہنچی۔
The party starts at midnight.
پارٹی آھی رات کو شروع ہوتی ہے۔
The meeting will finish at five-thirty.
اجلاس 530 پر ختم ہوگا۔
I will be there at noon.
میں دوپہر تھیٹر میں ہوگا۔
He does not like driving at night.
وہ شام کو ڈرائیونگ کرنا پسند نہیں کرتا ہے۔
I read my daughter’s story at beadtime.
میں شام کے وقت اپنی بیٹی کی کہانی پڑھی۔
Let’s talk about it at dinner tonight.
آج رات کھانے میں اس کے بارے میں بات کریں۔
She is working at the moment.
وہ اس وقت کام کررہی ہے۔
She is a little busy at present can I get her to call you back?
I finish the course at the end of April.
Extended
Since
FROM-TO
For
BY
Use of Since
- From a particular time in the past until a later time, or until now.
Examples
I have been studying since 9 am.
We had been playing the match since 9 o’ clock.
تم اکتوبر سے امتحان کی تیاری کر رہے تھے ۔
You had been preparing the speech since Monday.
تم منگل سے تقریر کی تیاری کر ہے تھے
The girls had not been washing the clothes since morning.
لڑکیاں صبح سے کپڑے نہیں دھو رہی تھیں۔
The lion had not been roaring in the zoo since evening.
شیر شام سے چڑیا گھر میں نہیں گرج رہاتھا۔
The boys had not been wasting his time since 2 o’clock.
لڑکا دو بجے سے اپنا ٹائم ضائع نہیں کر رہا تھا ۔
Use of For
- Used to show an amount of time.
He had been writing the letters for two hours.
وہ دو گھنٹے سے خط لکھ رہا تھا۔
I had been making this picture for one month.
میں ایک ماہ سے یہ تصویر بنا رہا تھا۔
People had been waiting for your return home for four years.
لوگ چار سالوں سے تمہاری وطن واپسی کا انتظار کر ہے تھے ۔
It had been raining for two days.
بارش دو دن سے ہو رہی تھی۔
The friends had not been talking for twenty minutes.
دوست بیس منٹ سے باتیں نہیں کر ہے تھے۔
Ali had not been doing his work for three days.
علی تین دن سے اپنا کام نہیں کرر ہا تھا۔

Preposition Of Verb
Definition:
A preposition verb is a combination of a verb and a preposition. It is simply a verb followed by a preposition
- Some verbs require specific prepositions to be used after the sentence. The combination of such a verb and its required position is called a prepositional verb
Examples:
She is suffering from a fever.
Don’t laugh at the poor.
She is looking at black-board
The dog is barking at a stranger.
She is waiting for him.
He is knocking at the door.
She is listening to music.
The kids are laughing at the joker.
We believe in God.
I agree with you.
 Prepositions and their Types with Urdu to English Examples PDF Download
Prepositions and their Types with Urdu to English Examples PDF Download
Get the Pdf of this lesson by the following link.

 Prepositions and their Types with Urdu to English Examples PDF Download
Prepositions and their Types with Urdu to English Examples PDF Download